• CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) the HTML elements you want to style.
• CSS selectors select HTML elements according to their id, class, type, attribute, etc.
We can divide CSS selectors into four categories:
• Simple selectors
• Combinator selectors (select elements based on a specific relationship between them)
• Pseudo selectors
• Attribute selectors (select elements based on an attribute or attribute value)**
In this article, we are going to discuss Simple selectors and Pseudo selectors.
Simple Selector
• Select elements based on name, id, and class.
• selects HTML elements based on the element name.
• The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element. To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
• The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute. To select elements with a specific class, write a period (.) character, followed by the class name.
pseudo-class selector
•pseudo-class is used to define a special state of an element.
•For example, it can be used to: -Style an element when a user mouses over it. -Style visited and unvisited links differently. -Style an element when it gets focus
Syntax-
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
Anchor Pseudo-classes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* unvisited link */
a:link {
color: red;
}
/* visited link */
a:visited {
color: green;
}
/* mouse over link */
a:hover {
color: #FF00FF;
}
/* selected link */
a:active {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Styling a link depending on state</h2>
<p><b><a href="default.asp" target="_blank">This is a link</a></b></p>
<p><b>Note:</b> a:hover MUST come after a:link and a:visited in the CSS definition in order to be effective.</p>
<p><b>Note:</b> a:active MUST come after a:hover in the CSS definition in order to be effective.</p>
</body>
</html>
The :first-child Pseudo-class
The:first-child pseudo-class matches a specified element that is the first child of another element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p:first-child {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is some text.</p>
<p>This is some text.</p>
<div>
<p>This is some text.</p>
<p>This is some text.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT

Pseudo-elements selectors
• A CSS pseudo-element is used to style specified parts of an element.
For example, it can be used to:
• Style the first letter, or line, of an element.
• Insert content before, or after, the content of an element.
SYNTAX
selector::pseudo-element {
property: value;
}
The ::before Pseudo-element
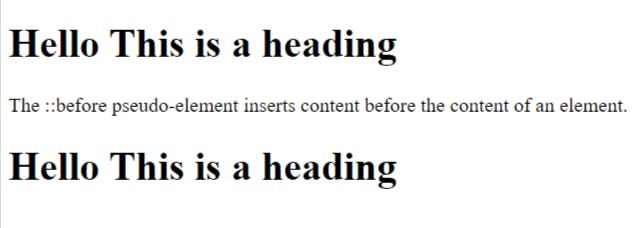
•The:: before pseudo-element can be used to insert some content before the content of an element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1::before {
content: "Hello ";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>The ::before pseudo-element inserts content before the content of an element.</p>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT
The ::after Pseudo-element
•The:: after pseudo-element can be used to insert some content after the content of an element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1::after {
content: " after hello";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>The ::after pseudo-element inserts content after the content of an element.</p>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT

These are some types of Selectors in CSS. Hope you like it and find it helpful.
Thank you :)


